1. 초기 세팅하기
먼저 vite를 이용해서 vanilla TS 파일을 만들어보자. 다음 명령어를 통해 Vanilla + TS 프로젝트의 초기 세팅의 도움을 받을 수 있다.
npm create vite@latest .
그리고 three.js 관련 의존성을 설치해주자.
npm i three --save
TypeScript를 쓸 것이고, Three.js에서는 아직 별도의 d.ts 파일을 제공해주지 않기 때문에 @types/three를 설치해주도록 하자
npm i --save-dev @types/three
이렇게 되면 초기 설정은 다 되었다.
2. 코드 작성
이제 코드를 작성해보도록 하자.
먼저 필요한 속성들과 생성자들을 작성해보도록 하자.
class App {
private renderer: THREE.WebGLRenderer;
private domApp: HTMLElement;
private scene: THREE.Scene;
private camera?: THREE.PerspectiveCamera;
private models: THREE.Object3D[] = [];
constructor(renderer: THREE.WebGLRenderer) {
this.renderer = renderer;
// 고해상도 모니터 처리하기
this.renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(2, window.devicePixelRatio));
// DOM에 렌더러의 domElement(Canvas) 추가
this.domApp = document.querySelector("#app") as HTMLElement;
this.domApp.appendChild(this.renderer.domElement);
// Scene 생성하기
this.scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 카메라, 광원, 물체 추가
this.setupCamera();
this.setupLight();
this.setupModels();
// 렌더링 코드 (애니메이션 + resize 이벤트)
this.setupEvents();
}
}
new App(
new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
antialias: true,
})
);
`this.renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(2, window.devicePixelRatio))`
- `window.devicePixelRatio`
브라우저에서 지원하는 속성으로, 현재 장치의 디스플레이 픽셀 비율을 나타낸다. 예를 들어, Retina 디스플레이를 사용하는 장치에서는 `window.devicePixelRatio`가 2나 그 이상이 될 수 있다.
- `Math.min(2, window.devicePixelRatio)`
이 부분은 두 값 중 작은 값을 반환한다. 여기서 2는 최대 픽셀 비율을 의미한다. 즉, window.devicePixelRatio가 2보다 크더라도 최대 픽셀 비율을 2로 제한하는 것이다. 이렇게 하는 이유는 성능 최적화와 관련이 있다. 너무 높은 픽셀 비율은 성능에 부담을 줄 수 있기 때문에 제한하는 것이라고 한다.
- `this.renderer.setPixelRatio(...)`
렌더러의 `setPixelRatio` 메서드는 렌더러가 사용할 픽셀 비율을 설정한다. 픽셀 비율을 설정하면 렌더링할 때 이미지가 더 선명하게 보일 수 있다.
`this.domApp.appendChild(this.renderer.domElement)`
- DOM에 렌더러의 domElement(Canvas)를 추가해준다.
이제 생성자 내부에서 필요한 코드들을 각각 작성해보도록 하자
1) 카메라 세팅
private setupCamera() {
const width = this.domApp.clientWidth;
const height = this.domApp.clientHeight;
this.camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, width / height, 0.1, 100);
this.camera.position.set(0, 0, 2);
}
2) 광원 세팅
private setupLight() {
const color = 0xffffff;
const intensity = 1;
const light = new THREE.DirectionalLight(color, intensity);
light.position.set(-1, 2, 4);
this.scene.add(light);
}
3) 모델 세팅
private setupModels() {
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1);
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0x44aa88 });
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
this.scene.add(cube);
this.models.push(cube);
}
4) 렌더링하는 함수 작성 (resize 이벤트, 애니메이션 + 렌더링)
private setupEvents() {
window.onresize = this.resize.bind(this);
this.resize(); // 브라우저는 처음 로딩될 때 resize 이벤트가 발생하지 않으므로 수동으로 호출
this.renderer.setAnimationLoop(this.render.bind(this)); // 애니메이션 + 렌더링
}
그렇다면 resize 관련 함수를 작성해보도록 하자. 카메라의 aspect를 변경해주고, renderer의 size를 변경해주는 코드를 작성해야 한다.
private resize() {
const width = this.domApp.clientWidth;
const height = this.domApp.clientHeight;
if (this.camera) {
this.camera.aspect = width / height;
this.camera.updateProjectionMatrix(); // 카메라의 속성이 변경되었을 때 내부 행렬을 업데이트
}
this.renderer.setSize(width, height);
}
render 함수를 작성해보자. 여기에는 시간에 따라 렌더링 결과를 변경하고, 화면을 렌더링하는 코드를 작성해야 한다.
private render(time: number) {
this.update(time);
this.renderer.render(this.scene, this.camera!);
}
시간에 따라 렌더링 결과를 변경하는 update 함수를 작성해보자
private update(time: number) {
const second = time / 1000; // 초단위로 변환
this.models.forEach((model) => {
model.rotation.x = second;
model.rotation.y = second;
});
}
이렇게 코드를 작성하면 결과물은 다음과 같다...!
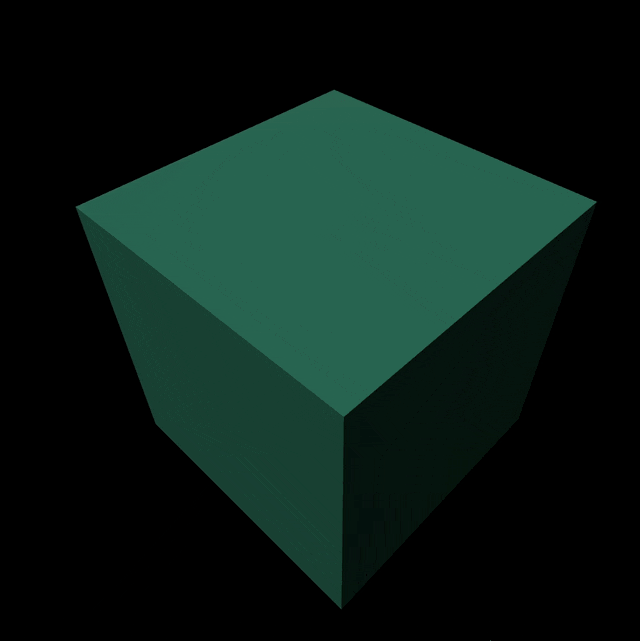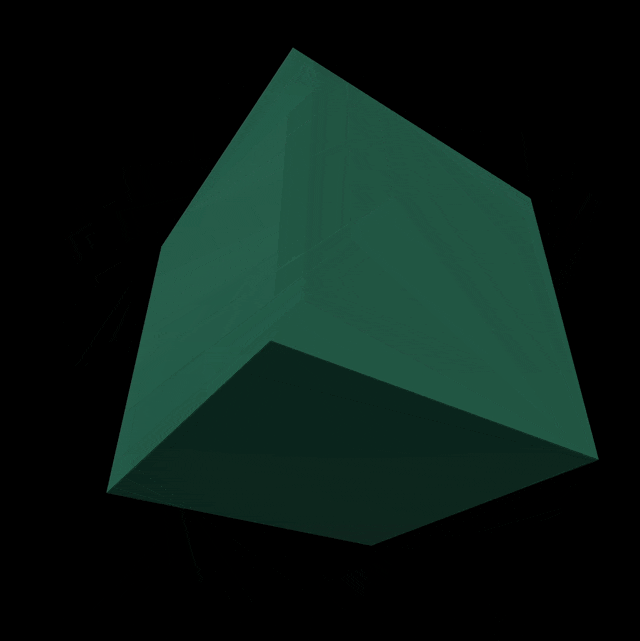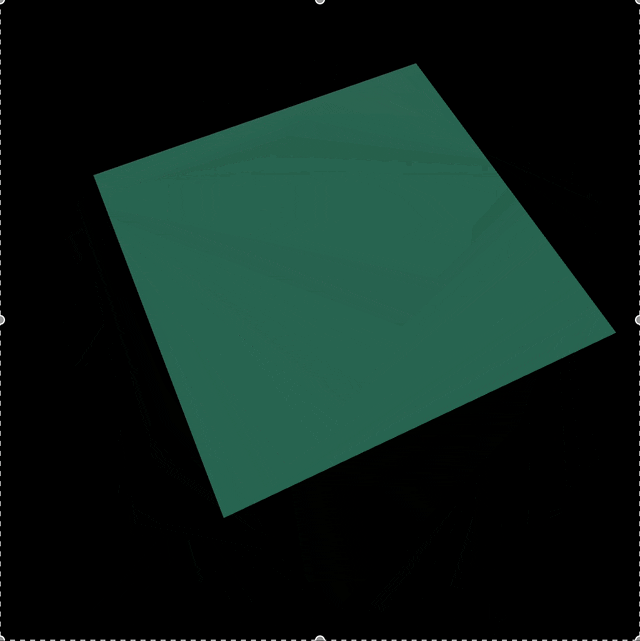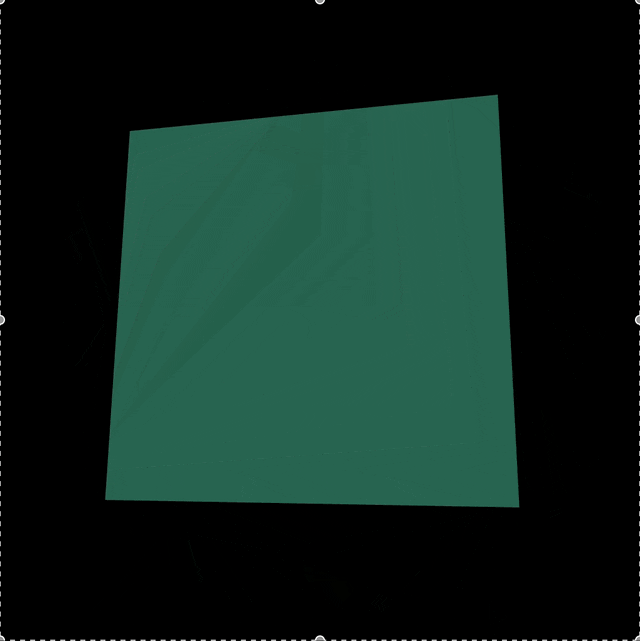
전체 코드는 다음과 같다
import "./style.css";
import * as THREE from "three";
// const root = document.querySelector("#app") as HTMLElement;
class App {
private renderer: THREE.WebGLRenderer;
private domApp: HTMLElement;
private scene: THREE.Scene;
private camera?: THREE.PerspectiveCamera;
private models: THREE.Object3D[] = [];
constructor(renderer: THREE.WebGLRenderer) {
this.renderer = renderer;
// 고해상도 모니터 처리하기
this.renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(2, window.devicePixelRatio));
// DOM에 렌더러의 domElement(Canvas) 추가
this.domApp = document.querySelector("#app") as HTMLElement;
this.domApp.appendChild(this.renderer.domElement);
//
this.scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 카메라, 광원, 물체 추가
this.setupCamera();
this.setupLight();
this.setupModels();
// 렌더링 코드 (애니메이션 + resize 이벤트)
this.setupEvents();
}
private setupCamera() {
const width = this.domApp.clientWidth;
const height = this.domApp.clientHeight;
this.camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, width / height, 0.1, 100);
this.camera.position.set(0, 0, 2);
}
private setupLight() {
const color = 0xffffff;
const intensity = 1;
const light = new THREE.DirectionalLight(color, intensity);
light.position.set(-1, 2, 4);
this.scene.add(light);
}
private setupModels() {
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1);
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({ color: 0x44aa88 });
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
this.scene.add(cube);
this.models.push(cube);
}
private setupEvents() {
window.onresize = this.resize.bind(this);
this.resize(); // 브라우저는 처음 로딩될 때 resize 이벤트가 발생하지 않으므로 수동으로 호출
this.renderer.setAnimationLoop(this.render.bind(this));
}
private resize() {
const width = this.domApp.clientWidth;
const height = this.domApp.clientHeight;
if (this.camera) {
this.camera.aspect = width / height;
this.camera.updateProjectionMatrix(); // 카메라의 속성이 변경되었을 때 내부 행렬을 업데이트
}
this.renderer.setSize(width, height);
}
private update(time: number) {
const second = time / 1000; // 초단위로 변환
this.models.forEach((model) => {
model.rotation.x = second;
model.rotation.y = second;
});
}
private render(time: number) {
this.update(time);
this.renderer.render(this.scene, this.camera!);
}
}
new App(
new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
antialias: true,
})
);